Understanding the concept of “coming together federation” is crucial for anyone interested in Indian politics and history. This term, often searched as “coming together federation meaning in Hindi,” refers to a specific type of federalism where independent states voluntarily unite to form a larger central government. This article delves into the nuances of this concept, its relevance in the Indian context, and its distinguishing features compared to other forms of federation. We’ll explore its historical roots, practical implications, and the benefits and challenges it presents.
A “coming together federation,” as opposed to a “holding together federation,” signifies a union born out of cooperation and mutual agreement. Think of it as independent entities choosing to pool their resources and sovereignty for a common good. This voluntary nature is a key characteristic that sets it apart. In India, this type of federation is enshrined in the Constitution, reflecting the historical context of its formation after independence.
Understanding “Coming Together” Federation
The essence of a “coming together federation” lies in its voluntary nature. States, initially independent and sovereign, decide to surrender some of their powers to a central authority. This act of coming together is driven by shared goals, such as enhanced security, economic prosperity, or improved governance. The United States and Switzerland are often cited as prime examples of this type of federation.
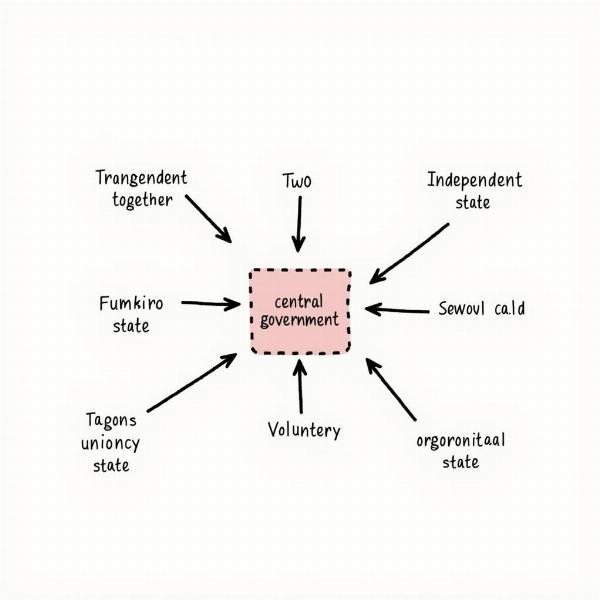 Diagram of Coming Together Federation
Diagram of Coming Together Federation
In India, the historical context surrounding independence played a significant role in shaping its federal structure. The integration of princely states into the newly formed nation exemplifies the “coming together” principle. These formerly independent states joined the Indian Union, thereby solidifying the federal structure.
Distinguishing “Coming Together” from “Holding Together” Federation
A key distinction lies in the distribution of power. In a “coming together” federation, the central government’s powers are often clearly defined and limited, with significant autonomy granted to the constituent states. Conversely, a “holding together” federation, like India, may feature a stronger central government with more extensive powers, often reflecting a need for greater unity and control.
This difference is reflected in the Indian Constitution, which grants certain exclusive powers to the Union government while also delineating powers shared between the Union and the states.
The Indian Context: A Unique Blend
While India is often described as a “holding together” federation due to its historical context and the need for a strong central government, elements of “coming together” are also evident. The integration of princely states, as mentioned earlier, reflects this principle. This blend of both forms of federation makes India’s case unique and complex.
Benefits and Challenges of “Coming Together” Federation
The benefits include increased cooperation among states, enhanced economic opportunities, and improved security. However, challenges can arise from potential conflicts between the central government and the states, particularly regarding the division of powers and resources.
Successfully navigating these challenges requires strong institutions, effective communication, and a shared commitment to the principles of federalism.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of “coming together federation meaning in Hindi” is essential for grasping the complexities of Indian federalism. While India’s model is a unique blend, the principles of voluntary union and shared governance remain fundamental. By acknowledging the historical context, practical implications, and ongoing challenges, we can appreciate the delicate balance that underpins India’s federal structure.
FAQ
- What is the main difference between “coming together” and “holding together” federations? The primary difference lies in the initial formation. “Coming together” federations arise from independent states voluntarily uniting, while “holding together” federations involve a pre-existing state decentralizing power to create constituent units.
- Is India strictly a “coming together” federation? No, India is primarily considered a “holding together” federation due to its historical context. However, the integration of princely states showcases elements of the “coming together” principle.
- Why is understanding this concept important? Comprehending this concept provides valuable insights into the dynamics of power sharing, state autonomy, and the overall functioning of the Indian government.
- What are the potential challenges of a “coming together” federation? Potential conflicts can arise between the central government and constituent states, especially regarding the division of powers and resources.
- What are the advantages of this type of federation? Advantages include increased cooperation among states, enhanced economic opportunities, and a stronger collective defense.
- How does “coming together” federation apply to India’s history? The integration of princely states after independence demonstrates the “coming together” aspect of Indian federalism.
- Where can I find more information on Indian federalism? You can explore academic resources, government publications, and online platforms specializing in Indian political science.
Meaning-Hindi.in is your premier destination for professional Hindi translation services, specializing in business, legal, technical, website localization, educational, and specialized translations. We offer accurate, culturally sensitive, and high-quality translations to bridge the language gap for businesses and individuals. Whether you need to translate legal documents, technical manuals, or marketing materials, our expert team delivers timely and reliable services. Contact us today for all your Hindi translation needs! Email: [email protected], Phone: +91 11-4502-7584. Connect with Meaning-Hindi.in today!